
Reverse Osmosis Wastewater Treatment
- Home
- »
- Products
- »
- Water & Wastewater Treatment Solution
- »
- Reverse Osmosis
What is Reverse Osmosis (RO)?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a powerful filtration method used in wastewater treatment that employs a semi-permeable membrane to remove ions, unwanted molecules, and larger particles from water. This process is driven by applying pressure to the water being treated and forcing it through the RO membrane. The membrane's pores are small enough to block contaminants and allow only clean water to pass through, effectively reducing the presence of dissolved salts, bacteria, and organic substances.
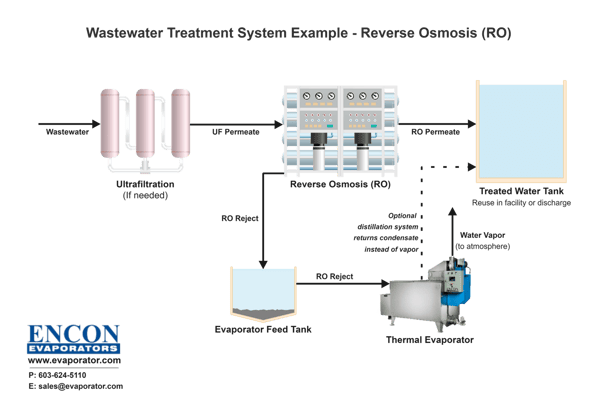
RO produces a permeate stream (purified water) and a concentrate stream (reject stream). The reverse osmosis (RO) reject is typically evaporated or hauled away for disposal.The permeate stream is typically reused in the facility's process or discharged to the sewer or environment.
When should I implement a Reverse Osmosis (RO) system?
Many industries require high-purity water for their processes. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, power generation, and food and beverage production utilize reverse osmosis (RO) to meet strict water quality standards.
Because RO can also treat wastewater to a high enough quality to meet standards for discharge or reuse, reducing the demand on freshwater resources. This is particularly relevant in water-scarce regions or for facilities aiming to achieve zero liquid discharge (ZLD) by recycling water.
Another common application of RO is to reduce the volume of wastewater prior to downstream treatment such as thermal evaporation processes.
Typical Industrial Wastewater ZLD Applications:
- Metal working wastewater reclamation
- Cannabis cultivation fertigation wastewater
- Surface finishing wastewater
- Plastics manufacturing wastewater
- Power plant FGD wastewater
- Chemical manufacturing wastewater
- Pharmaceutical wastewater
- Food & Beverage wastewater reuse
- Paper plant effluent

Full Range of Upgrades, Accessories and Services to Unlock Your Evaporator’s Full Potential

ENCON offers a full range of upgrades, accessories and services to minimize labor and maximize return on investment.
Recover your wastewater as clean condensate with our condenser package!
Work with our consultative Sales Engineers to spec a turn-key system.
Utilize our air permitting / permit-exemption services.
Automate with auto-dump or auto-oil-decant.
Free Application Feasibility Report
The centerpiece of our consultative approach is our complimentary bench scale analysis of your waste or process stream. This free analysis determines:
- How appropriate the stream is for evaporation
- Estimated reduction percentage
- Recommended materials of construction
- Recommended operating procedures.

Why Choose ENCON?
Superior Service & Support – We provide industry-leading technical support, ensuring customers receive prompt and knowledgeable assistance.
Consultative Sales Approach – Our expert sales engineers guide you through the process, including a detailed boil analysis of your waste stream to tailor the perfect evaporator solution.
Proven Industry Experience – With over 2,000 installations worldwide, ENCON evaporators are trusted by some of the largest companies, including 3M, GM, Ford, and Caterpillar, for their reliability and performance.
Wide Range of Heat Source Options – The most extensive selection of heat sources in the industry, ensuring the most cost-effective solution for any application.
Largest Thermal Evaporators in the Market – Designed to handle the most demanding industrial needs, with larger capacities than competitors. Proudly designed and manufactured in the USA.
Unmatched Reliability & Performance – ENCON evaporators are built for longevity, offering superior technical advantages and reliability over competitors.